In the United States, whilst the INBDE is a federal exam, each state has its own requirements for allowing dentists to practice. To become licensed as a dentist in a particular state, you must typically:
Graduate from a dental education program accredited by the Commission on Dental Accreditation (CODA).
Pass the National Board Dental Examination (NBDE), which is a comprehensive assessment of dental knowledge and clinical skills that is required for licensure in most states.
Pass a state-specific licensure exam, which may be the NBDE Part II or a different exam.
Meet any other requirements set by the state dental board, such as completing a certain number of hours of supervised practice or completing continuing education (CE) requirements.
To maintain a dental license, dentists must typically complete a certain number of CE hours each year and meet any other requirements set by their state dental board.
It is important to note that the requirements for dental licensure vary by state, so you should check with the dental board in the state where you wish to practice for specific information on their licensure requirements.
Below is an image detailing out the differences between the state requirements.
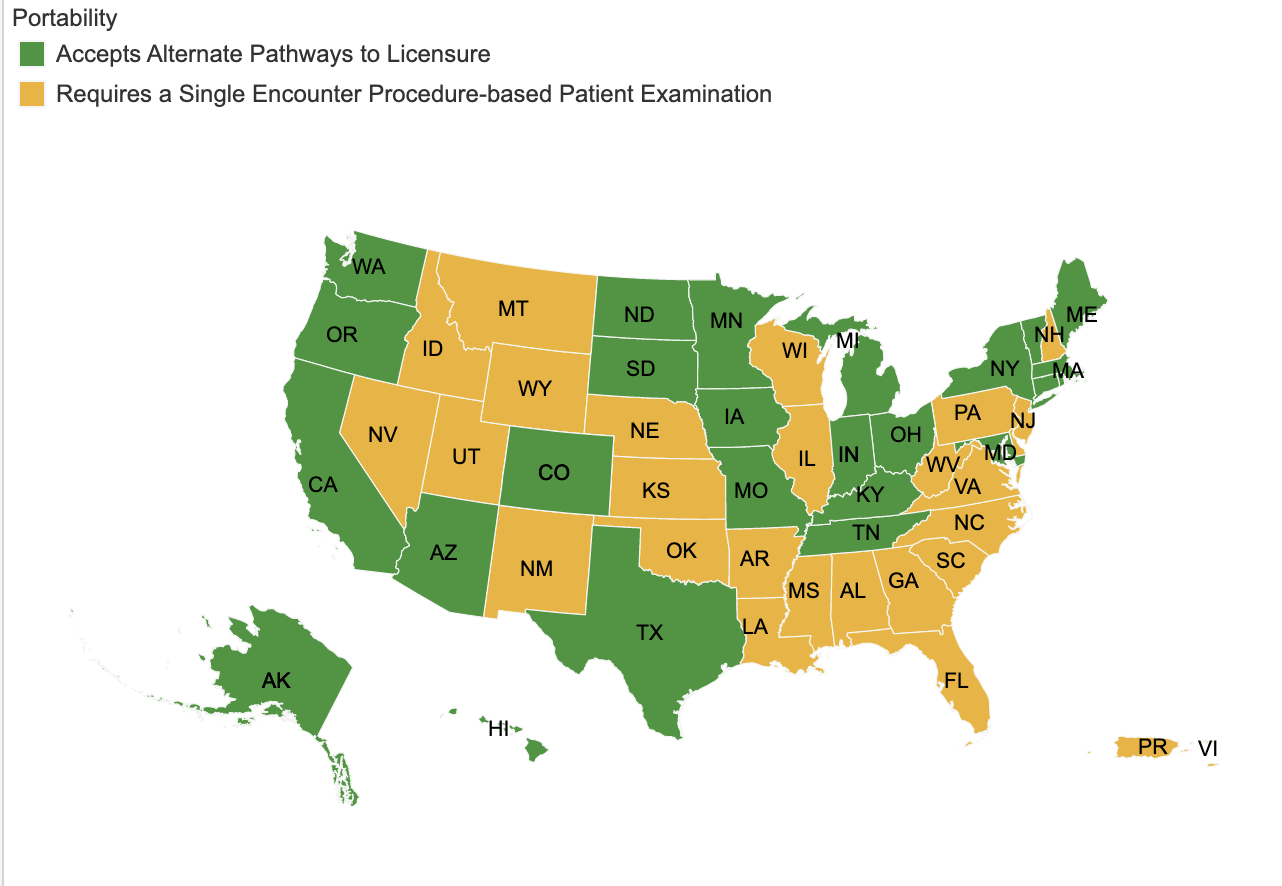
If you would like a more interactive map to see what exactly is needed for each state, use the official ADA map.
